Digital Operational resilience
Cyber resilience is playing an increasingly important role, especially for (financial) companies. In its 2023 status report on IT security in Germany, the BSI explains, among other things, the continuing rise in cyber threats, which are at an unprecedented high [1]. One of the factors contributing to this is the professionalization of cybercrime.
However, cyber risks are not only on the rise in Germany, but also across Europe. Consequently, cyber resilience is also a focus for various supervisory authorities [2].
In order to increase cyber resilience in the EU and at individual financial companies, the regulation and an accompanying directive on digital operational resilience were developed and published, which will be binding in all member states from January 2025.
Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA)
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) aims to increase the digital resilience of companies in order to take account of the increasing importance of ICT systems. It is also intended to enable companies to react quickly to potential threats.
In terms of content, the European legal act deals with the management of increasing dependencies and interdependencies within the financial sector, but also with service providers and infrastructures. It is intended to focus more on ICT security and digital resilience as components of operational risk. As part of this, national requirements will be harmonized and the complexity of existing requirements reduced.
impact analysis
To make it easier for you to get to grips with the topic, we have taken a closer look at the DORA regulation and the accompanying directive.
In doing so, we have looked at its addressees, potentially affected areas of a financial company, the conceivable implementation effort and the implementation period.
We also looked at the delegated acts that further detail DORA.
The DORA Regulation (EU) 2022/2554 sets out the substantive rules, which we will look at in more detail below.
The aim is to improve digital resilience both at the level of institutions and at the level of the financial system as a whole.
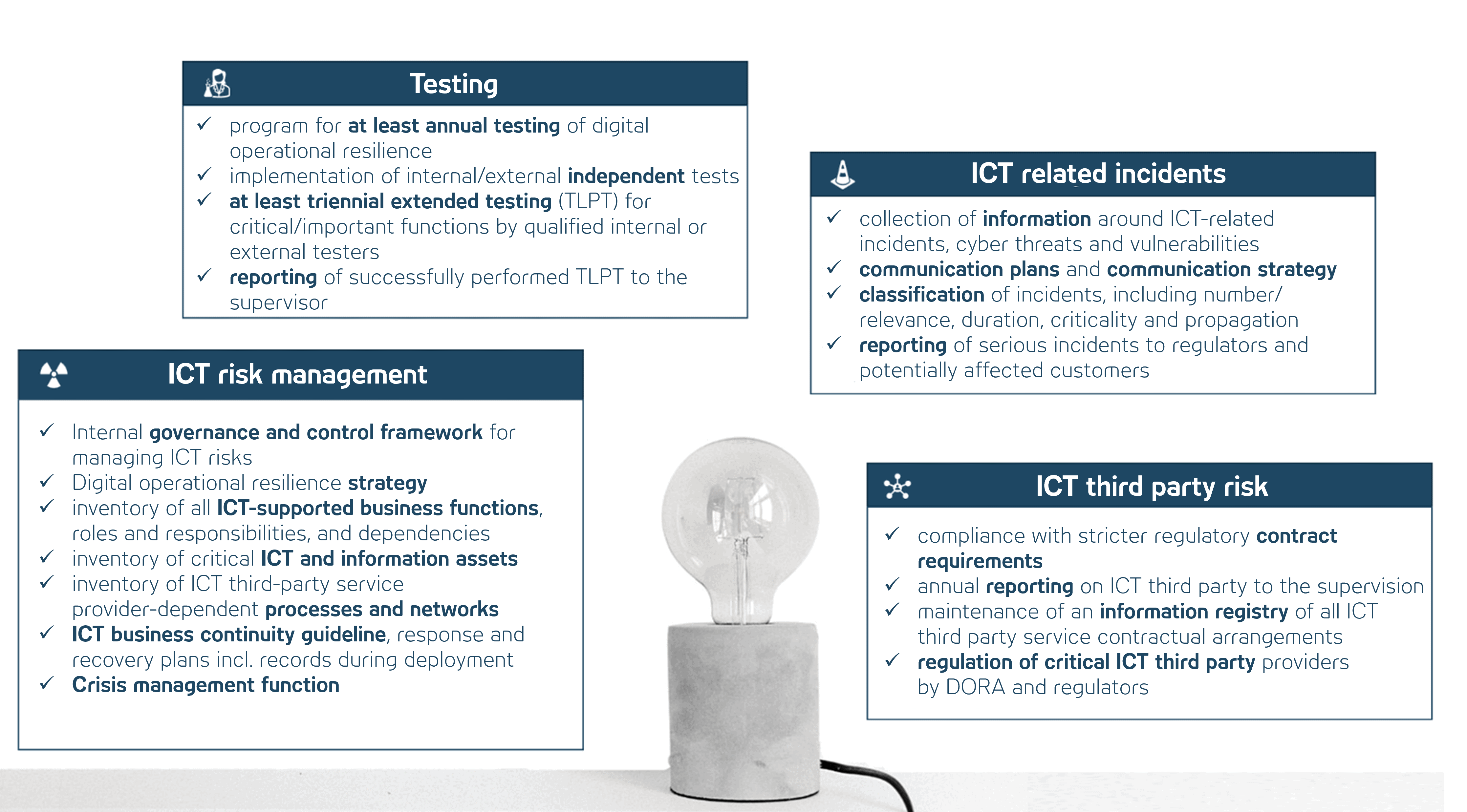
Focus in the context of information and communication technology (ICT)
- Risk management
- Threat and incident management
- Test management
- Crisis and emergency management
- Third-party risk management
- Information exchange
The DORA Directive (EU) 2022/2556 makes the necessary changes to the existing regulatory frameworks at EU level. The existing frameworks do not yet adequately address digital operational resilience and are therefore being expanded.
Content expansion of the
Addressees
- Banks
- Financial service providers
- Securities institutions
- Insurance companies
- Pension funds
- KVGs
- Investment funds
- ICT third-party service providers
Affected Areas
- Risk management
- Governance
- Corporate management
- Outsourcing management
- Provider management
- Strategy
- Reporting
- Information Security
- Legal & Compliance
- Process Management
- IT Strategy & Governance
- Emergency Management
- Communication
- Internal Audit
- Test Management
Implementation Effort
Overall medium, provided that compliance with the minimum requirements for risk management and proper management as well as the regulatory requirements for IT are met.
| Risikomanagement | medium |
| Threat and incident management | medium bis high |
| Testmanagement | medium bis high |
| Crisis and emergency management | medium bis high |
| Third-party risk management | high |
| Exchange of information | low |
Dates and times
Entry into force: 17.01.2023
Start of validity: 17.01.2025
As a regulation, the requirements will also apply directly to financial companies and ICT service providers in Germany from January 2025. As part of the Financial Market Digitization Act [5], the directive will also be transposed into national law and will result in amendments to the German Banking Act (KWG), the German Insurance Supervision Act (VAG), the German Securities Supervision Act (ZAG), the German Investment Code (KAGB) and several other laws.
ORA addresses various topics and therefore affects many areas in financial companies. The group of institutions exempt from the regulation is also manageable.
Bulletproofing Your Business
Use our checklist to see if you are already in compliance with DORA requirements to identify your need for action by 2025.
In our checklist we present the requirements of the DORA. It also includes an assessment of which requirements are already anchored in the same or a similar form by other regulatory requirements. Have we sparked your interest? Then take this opportunity to stay up to date on regulatory changes around IT security.
Get access to our free checklist.
Sources:
- https://bsi.bund.de/DE/Service-Navi/Publikationen/Lagebericht/lagebericht_node.html
- EIOPA: https://www.eiopa.europa.eu/macro-markets-and-digitalisation-risks-are-insurers-top-concern-according-eiopas-insurance-risk-2023-11-06_en,
ESMA: https://esma.europa.eu/press-news/esma-news/esma-put-cyber-risk-new-union-strategic-supervisory-priority,
EBA: https://www.eba.europa.eu/eba-publishes-its-work-programme-2024,
ESAs: https://www.eba.europa.eu/esas-publish-joint-committee-work-programme-2024 - https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2022/2554/oj
- https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2022/2556/oj
- https://www.bundesfinanzministerium.de/Content/DE/Gesetzestexte/Gesetze_Gesetzesvorhaben/Abteilungen/Abteilung_VII/20_Legislaturperiode/2023-10-23-FinmadiG/0-Gesetz.html